Ameloot Group
Manipulating Porous Matter
Papers
Transport diffusion measurements in ZIF-8 thin films by quartz crystal microgravimetry: pitfalls and opportunities @Advanced Functional Materials

Mass transport in nanoporous materials directly affects their performance in applications, as seen in adsorption-based separations where diffusion kinetics limit the maximum production rate. Nevertheless, diffusion kinetics have been understudied, largely due to the difficulties in measuring them accurately. Under well-defined conditions, gravimetric uptake experiments are well-suited for studying the mass transfer behavior of guests in nanoporous materials.
In this work, we illustrate the pitfalls and opportunities in the experimental determination of intrinsic transport diffusivities by microgravimetry. To do so, the behavior of a series of alcohols (n-propanol, n-butanol), ketones (acetone, butanone), and alkanes (n-pentane, n-hexane) was studied in ZIF-8 thin films deposited on quartz crystal microbalance sensors. For all studied guest molecules, the sorption rate proved strongly concentration-dependent, resulting in diffusivity values spanning several orders of magnitude. Using this data set, we illustrate how erroneous conclusions can easily result when insufficient care is taken in acquiring or analyzing the uptake data. To prevent such issues, which are unfortunately common in reported data, a set of guidelines was formulated to extend the IUPAC recommendations for diffusion measurements to the specific case of quartz crystal microgravimetry. These guidelines cover the setup, the adsorbent, the experimental design to elucidate the model requirements, heat and bed effects, and the contribution of surface barriers. At the same time, the novel data reported here substantially broadens the existing knowledge of transport diffusion in ZIF-8. Read our work here!
Kinetic selectivity in metal-organic framework chemical sensors @Nature Communications
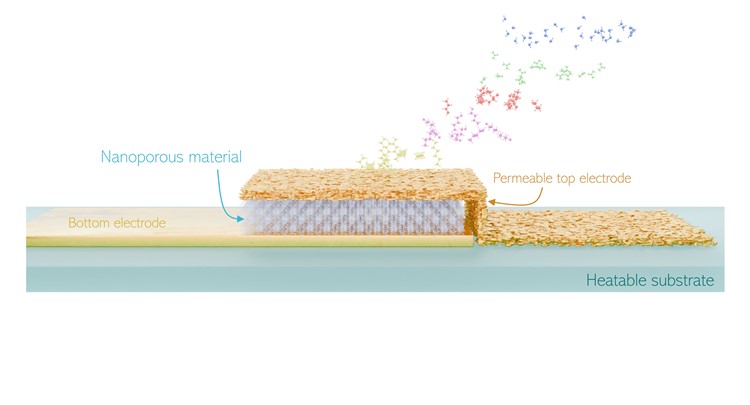
Despite the enormous potential of gas sensors in health, safety, and environmental applications, current technologies fall short in terms of selectivity and miniaturization for everyday use. Our latest work, now published in Nature Communications, tackles this challenge by integrating nanoporous materials that distinguish gases based on how quickly they travel through the pores. For the first time, we introduce the kinetic selectivity achievable in nanoporous crystals into the domain of chemical sensors. With just one sensor, we can differentiate and quantify ppm-level VOC mixtures, even under high humidity, outperforming a commercial electronic nose. This novel platform technology opens the door to a wide range of VOC applications. Read our work here!
💡 Curious about kinetic selectivity sensing? Explore our tech offer and watch our explainer video.
We are refining our technology to specific applications-driven challenges, and would greatly value your input and perspective. Can we solve your detection problem? Let’s talk: [email protected]
Oriented and Area-Selective Growth of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 Films by Molecular Layer Deposition @Chemistry of Materials

Integrating metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) into microfabrication processes will benefit from controlled vapor-phase deposition techniques. This study presents a molecular layer deposition method that enables area-selective and oriented growth of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) films. Substrates functionalized with self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) with different end groups (alkyl, phenyl, hydroxyl, carboxyl, amine, and imidazole) allow tuning the degree of crystallographic orientation in the resulting MOF layers. Spatial control over SAM formation determined the surface mobility of the ZIF-8 building blocks, which enabled area-selective deposition.
Want to know more? 💡
Consult this paper in the Scientific Highlights of the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) or read the full article here.
Adsorption-Based Electrochemical Sensor Design for the Aqueous Detection of Paracetamol @Advanced Engineering Materials
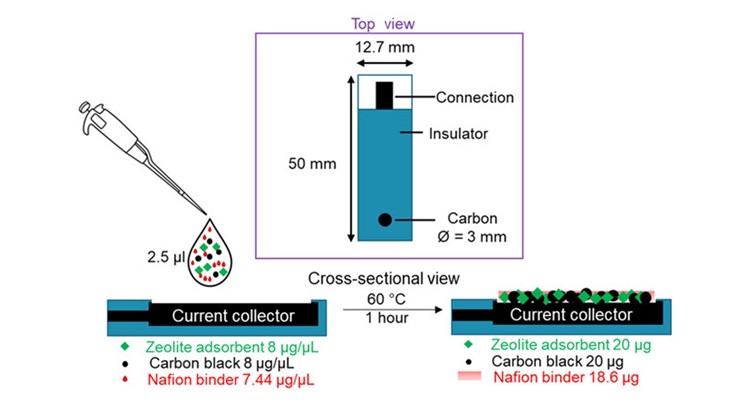
This study investigates the critical role of adsorption in the development of electrochemical sensors, focusing on carbon (Vulcan XC72R, acetylene black, and graphite) and zeolite (high-silica ZSM-5 and all-silica zeolite β) materials. Based on the paracetamol adsorption characteristics of these materials, an optimized disposable electrochemical sensor is created. This sensor exhibits a linear range of up to 5 μM and a remarkable detection limit of 150 nM (S/N = 3), ≈1000-time improvement over the blank sensor. Moreover, paracetamol can be measured selectively because glucose has no adsorption affinity for the selected sensor materials. These findings underscore the significance of adsorption properties in sensor material selection in enhancing sensitivity and robustness against interfering species.
More information can be found here, or on our publication page.
Systematic design and functionalisation of amorphous zirconium metal–organic frameworks @Chemical Science
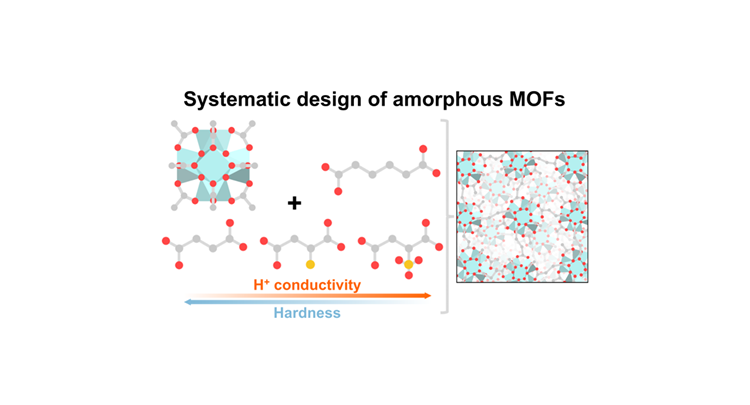
Controlling the structure and functionality of crystalline metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) using molecular building units and post-synthetic functionalisation presents challenges when extending this approach to their amorphous counterparts (aMOFs). Here, we present a new bottom-up approach for synthesising a series of Zr-based aMOFs, which involves linking metal–organic clusters with specific ligands to regulate local connectivity. In addition, we overcome the limitations of post-synthetic modifications in amorphous systems, demonstrating that homogeneous functionalisation is achievable even without regular internal voids. By altering the acidity of the side group, length, and degree of connectivity of the linker, we could control the porosity, proton conductivity, and mechanical properties of the resulting aMOFs.
More information can be found here, or on our publication page.
Mind the Gap: The Role of Mass Transfer in Shaped Nanoporous Adsorbents for Carbon Dioxide Capture @JACS!
Adsorptive separations by nanoporous materials are major industrial processes. The industrial importance of solid adsorbents is only expected to grow due to the increased focus on carbon dioxide capture technology and energy-efficient separations. To evaluate the performance of an adsorbent and design a separation process, the adsorption thermodynamics and kinetics must be known. However, although diffusion kinetics determine the maximum production rate in any adsorption-based separation, this aspect has received less attention due to the challenges associated with conducting diffusion measurements. These challenges are exacerbated in the study of shaped adsorbents due to the presence of porosity at different length scales. As a result, adsorbent selection typically relies mainly on adsorption properties at equilibrium, i.e., uptake capacity, selectivity and adsorption enthalpy.
In this Perspective, based on an extensive literature review on mass transfer of CO2 in nanoporous adsorbents, we discuss the importance and limitations of measuring diffusion in nanoporous materials, from the powder form to the adsorption bed, considering the nature of the process, i.e., equilibrium-based or kinetic-based separations. By highlighting the lack of and discrepancies between published diffusivity data in the context of CO2 capture, we discuss future challenges and opportunities in studying mass transfer across scales in adsorption-based separations.
More information can be found here, or on our publication page.
Our 3D printed ferromagnetic passive shims on the cover of JMR!

A visualization of our paper '3D printing of ferromagnetic passive shims for field shaping in magnetic resonance imaging' on the cover of Journal of Magnetic Resonance!
Find the article here or on the publication page of the website.
3D printing of ferromagnetic passive shims for field shaping in magnetic resonance imaging
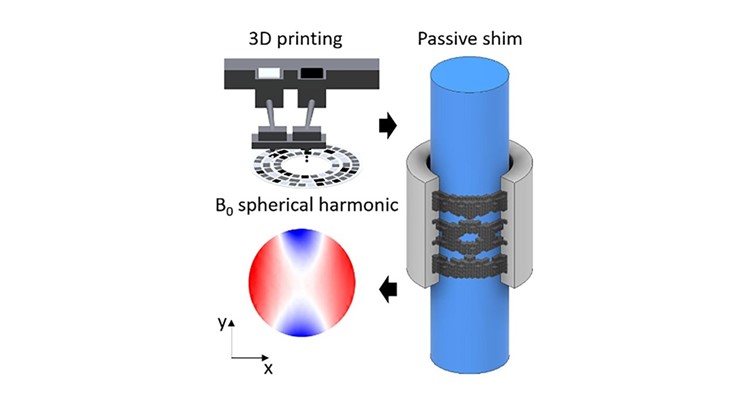
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) often encounters image quality degradation due to magnetic field inhomogeneities. Conventional passive shimming techniques involve the manual placement of discrete magnetic materials, imposing limitations on correcting complex inhomogeneities. To overcome this, we propose a novel 3D printing method utilizing binder jetting technology to enable precise deposition of a continuous range of concentrations of ferromagnetic ink. This approach grants complete control of the magnitude of the magnetic moment within the passive shim enabling tailored corrections of B0 field inhomogeneities. By optimizing the magnetic field distribution using linear programming and an in-house written Computer-Aided Design (CAD) generation software, we printed shims with promising results in generating low spherical harmonic corrections.
Experimental evaluations demonstrate feasibility of these 3D printed passive shims to induce target magnetic fields corresponding to second-order spherical harmonic, as evidenced by acquired B0 maps. The electrically insulating properties of the printed shims eliminate the risk of eddy currents and heating, thus ensuring safety. The dimensional fabrication accuracy of the printed shims surpasses previous methods, enabling more precise and localized correction of subject-specific inhomogeneities. The findings highlight the potential of binder-jetted 3D printed passive shims in MRI shimming as a versatile and efficient solution for fabricating passive shims, with the potential to enhance the quality of MRI imaging while also being applicable to other types of Magnetic Resonance systems.
Check out a visualization of this article on JMR cover!
More information can be found here, or on our publication page.
From Grayscale Photopolymerization 3D Printing to Functionally Graded Materials
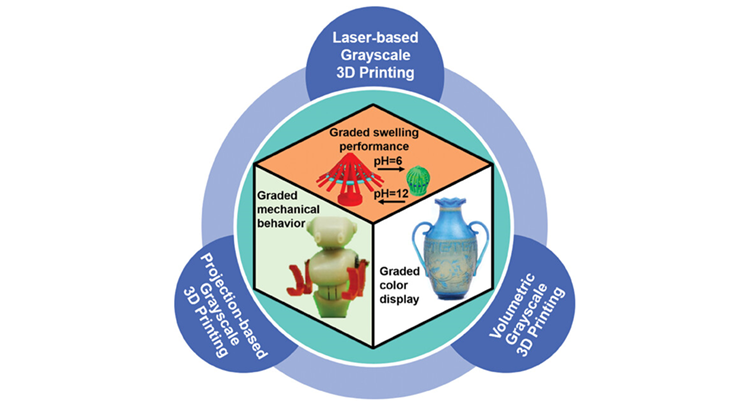
Functionally graded materials (FGMs) have spatial variations in structure or composition that result in gradients in their mechanical, thermal, swelling, or other properties. FGMs have garnered significant research interest because of their extensive applications in areas such as biomedical implants, sensors, and soft robotics. Recently, grayscale photopolymerization 3D printing has emerged as a promising technology for crafting complex and high-resolution FGMs.
This comprehensive work delves into various grayscale photopolymerization 3D printing techniques, offering insights into their ability to precisely control printing exposure energy and polymerization degree, which in turn influence material properties. Furthermore, this work highlights diverse applications of grayscale vat-photopolymerization 3D printing. Finally, it offers perspectives on ways to enhance grayscale photopolymerization 3D printing, with a focus on improving printing feedstocks and grayscale strategies.
More information can be found here, or on our publication page
3D Printed Power Source for Point-of-Care Diagnostics @Advanced Engineering Materials!
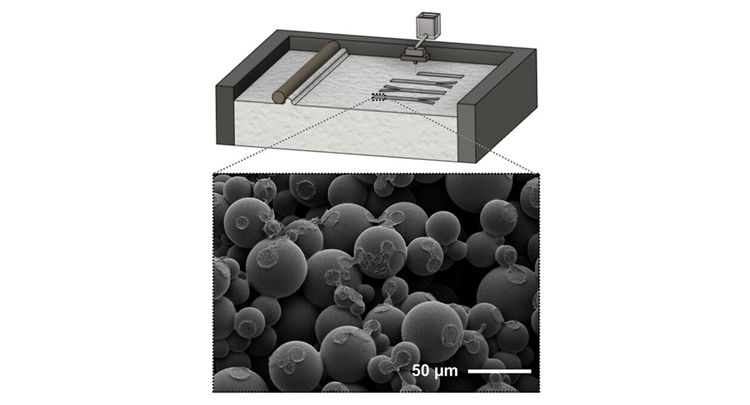
Point-of-care (POC) devices require more advanced detection techniques than those currently available to achieve enhanced quantification and sensitivity. Incorporating a micro power supply could be a viable solution to enable the implementation of these techniques. In recent years, paper-based microfluidic galvanic cells (μGCs) have emerged as promising disposable power sources; however, the fabrication process remains labor intensive.
This study demonstrates the potential of three-dimensional printing as a novel fabrication method for μGCs. The autonomous μGCs are fabricated using a powder-based 3DPed method, resulting in a porous body in which capillary forces enable the coflow of redox-active solutions. As a proof of concept, a handheld glucometer is powered by coupling four μGCs in series.
More information can be found here, or on our publication page